Kidney disease is often referred to as a silent epidemic, affecting millions worldwide without them even realizing it. The kidneys, two bean-shaped organs located on either side of the spine at the lower back, play an essential role in filtering waste from the blood, regulating blood pressure, and maintaining electrolyte balance. However, when these vital organs falter, the ramifications can be severe, leading to chronic kidney disease (CKD) or even renal failure. Understanding kidney disease symptoms, the causes, and how to manage this condition is crucial for proactive health measures.

Where Are Your Kidneys Located?
Before delving into the complexities of kidney disease, it’s essential to understand where your kidneys are located. The kidneys reside at the back of the abdominal cavity, protected by the rib cage. They are approximately the size of a fist and sit about an inch below the ribcage. Knowing the anatomy of these organs helps individuals better understand where to feel for any discomfort related to kidney issues. When kidney problems arise, people may experience pain in the lumbar region or exhibit kidney infection symptoms such as fever and fatigue, prompting further investigation.

What Causes Kidney Disease?
Understanding the etiologies behind kidney disease is fundamental in preventing its development. There are numerous causes of kidney disease, ranging from diabetes and high blood pressure to genetic factors and excessive use of substances toxic to the kidneys. Conditions such as urinary tract infections can also lead to a decline in kidney health. It’s vital to recognize that lifestyle choices play a significant role; dietary habits, smoking, and insufficient hydration contribute to kidney damage over time.
Transitioning from understanding causes, it becomes evident that awareness can drive preventive measures. By prioritizing regular health check-ups and engaging in a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, individuals can shield their kidneys from potential damage.
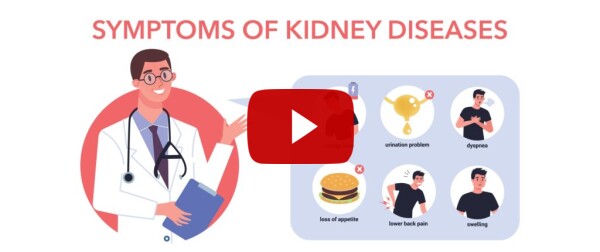
Recognizing Kidney Disease Symptoms
Spotting kidney disease symptoms early can be life-saving. Common symptoms include fatigue, swelling in the ankles or feet, changes in urination frequency, and persistent back pain. Notably, kidney disease symptoms in females can often differ from those in males, emphasizing the need for female-centric health awareness. Additionally, other symptoms such as appetite loss, nausea, or dizziness should not be overlooked.
Moreover, recognizing early signs can lead to timely interventions. For instance, knowing what is the first sign of kidney problems could lead to an early diagnosis and significantly improve the management of chronic kidney disease (CKD).

Acute vs. Chronic Kidney Disease
It is essential to distinguish between acute renal failure and chronic kidney disease because the diagnostic and treatment approaches vary significantly. Acute renal failure can occur suddenly, often due to a medical emergency such as dehydration or a heart attack. Meanwhile, chronic kidney disease develops gradually over time, often spanning years, making it essential to understand the differences between CKD symptoms and those associated with acute renal failure.
Each type requires a clinical approach tailored to its unique characteristics. For chronic kidney disease symptoms, healthcare providers focus on long-term management strategies to slow down progression, while acute renal failure necessitates immediate interventions to restore kidney function.
Signs of Kidney Failure – What to Look For
When kidneys fail, the body exhibits clear signs that should not be ignored. Symptoms of kidney failure might include a reduced amount of urine, swelling due to fluid retention, and difficulty breathing. Patients may also experience fatigue, confusion, and significant fluctuations in blood pressure. It’s crucial to actively monitor these indicators, as recognizing signs of kidney problems can facilitate timely medical attention.
Emotionally, the journey through kidney failure can be overwhelming. The challenges associated with managing kidney function often require a robust support system, both from healthcare professionals and caregivers. Transitioning to effective communication with loved ones can ease the emotional burdens, making the management of kidney disease easier to navigate.

Chronic Kidney Disease – Stages and Symptoms
Chronic kidney disease exists in stages, ranging from stage 1 to stage 5, with stage 5 being end-stage renal disease requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant. Symptoms of CKD can vary significantly depending on the stage, with early stages often presenting subtle signs, which makes routine testing essential. Common indications include changes in urine appearance, swelling, and high blood pressure.
Moreover, understanding the stages – what chronic kidney disease specifically encompasses – is vital for patients and their families. The CKD stages offer insight into potential interventions and necessary lifestyle adjustments that can positively impact kidney health. Patients often ask, “How do I know if I have kidney disease?” The answer lies in routine screenings that measure kidney function.

The Role of Lifestyle in Kidney Health
Lifestyle choices are paramount in preventing and managing kidney diseases. Maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding substances that can cause kidney damage, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can significantly alter the course of kidney health.
Additionally, managing underlying conditions such as hypertension and diabetes is critical. These chronic conditions are leading causes of kidney disease, making their careful management essential in averting renal failure. A healthy lifestyle is not about radical changes but rather consistent, small adjustments over time.

Treatment Options for Kidney Disease
Management strategies for kidney disease vary depending on the stage and severity of the condition. Treatments range from lifestyle modifications and medication to more intensive interventions like dialysis and kidney transplants.
For those with early-stage kidney disease, monitoring and controlling blood pressure and glucose levels can often improve outcomes. In advanced stages, healthcare providers may recommend renal replacement therapy. Understanding the phrase “what does kidney failure feel like” underlines the importance of patient awareness and advocacy in seeking appropriate treatment options.

Living with Kidney Disease – Coping Mechanisms and Support
Living with kidney disease can be challenging, requiring not just medical management but also emotional and psychological support. Patients should reach out to support groups to share their experiences, enabling them to connect with others facing similar challenges. This connection serves as a reminder that they are not alone in their journey.
Furthermore, mental health cannot be underestimated. Regular counseling sessions can help manage mental health issues that emerge from living with a chronic illness. The path to living well with kidney disease involves a holistic approach that combines medical care with psychological well-being.

Conclusion – Taking Control of Kidney Health
In conclusion, kidney disease presents a myriad of challenges, but it is not insurmountable. By understanding the anatomy, causes, symptoms, and treatments available, individuals can take proactive steps to safeguard their kidney health. Ultimately, knowledge is power. Awareness of the symptoms of kidney disease, recognition of lifestyle influences, and seeking support can empower individuals to manage their kidney conditions effectively.
